Introduction:
Obesity is a complex and prevalent health condition characterized by an excess accumulation of body fat. It is a significant global health concern that can lead to a range of serious health issues, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and certain cancers. Identifying the warning signs of obesity is crucial for early intervention and prevention. In this article, we will explore the definition of obesity, its causes, and the warning signs that indicate an individual may be at risk.
Understanding Obesity:
Sedentary Behavior:
A predominantly sedentary lifestyle, characterized by prolonged periods of sitting or inactivity, is closely linked to obesity. Lack of physical activity can contribute to weight gain and metabolic imbalances.
Unhealthy Eating Habits:
Poor dietary choices, such as consuming excessive amounts of processed foods, sugary beverages, and high-calorie snacks, can contribute to obesity. Emotional eating and a lack of portion control are also warning signs.
Psychological and Emotional Signs:
Obesity is commonly defined by the Body Mass Index (BMI), a measure calculated by dividing a person's weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters. A BMI of 30 or higher is generally considered indicative of obesity. However, it's essential to note that BMI is a general guideline and may not accurately reflect an individual's health status, as it does not consider factors such as muscle mass and distribution of fat.
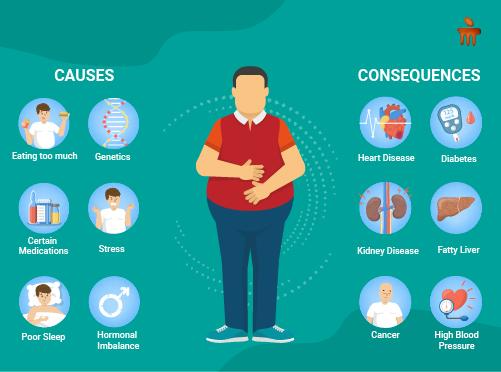
Causes of Obesity:
Obesity is a multifaceted condition influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and behavioral factors. Poor dietary choices, sedentary lifestyles, genetic predisposition, and certain medical conditions contribute to the development of obesity. Additionally, psychological factors like stress, depression, and lack of sleep can also play a role in weight gain.
Warning Signs of Obesity:
BMI Measurement:
A BMI of 30 or higher indicates obesity, but it is important to interpret this value in conjunction with other factors for a comprehensive assessment.
Increased Waist Circumference:
Excess fat accumulation around the abdominal area, often measured by an increased waist circumference, is a significant warning sign of obesity. In men, a waist circumference above 40 inches, and in women, above 35 inches, may indicate an increased risk.
Unexplained Weight Gain:
Sudden and unexplained weight gain, especially if accompanied by changes in lifestyle, can be a sign of obesity. This is particularly relevant if the weight gain occurs despite efforts to maintain a healthy diet and exercise routine.
Physical Symptoms:
Obesity can manifest physically with symptoms such as difficulty breathing, joint pain, and fatigue. These symptoms may interfere with daily activities and indicate the need for medical attention.
Health Conditions:
The presence of obesity-related health conditions like high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, and sleep apnea can serve as warning signs of obesity. Regular health check-ups are essential for early detection and management.
Lifestyle Indicators:
Depression and Stress:
Mental health plays a significant role in weight management. Chronic stress and depression can lead to emotional eating and a sedentary lifestyle, contributing to weight gain over time.
Body Image Issues:
Negative body image and dissatisfaction with one's appearance may contribute to unhealthy weight management practices, including extreme diets or unhealthy eating behaviors.
Social and Environmental Factors:
Socioeconomic Status:
Individuals with lower socioeconomic status may have limited access to nutritious foods and recreational facilities, increasing the risk of obesity. Economic factors can influence lifestyle choices and contribute to weight-related issues.
Environmental Influences:
Living in environments with limited opportunities for physical activity, such as areas lacking parks or safe spaces for exercise, can contribute to obesity. Access to healthy food options also plays a role in weight management.
Family History:
Genetic Predisposition:
Family history can influence an individual's susceptibility to obesity. If close relatives have a history of obesity-related conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, it may increase one's risk of developing obesity.
Medical Conditions:
Hormonal Imbalances:
Certain medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can lead to hormonal imbalances that contribute to weight gain. Identifying and addressing these conditions is crucial for effective weight management.
Seeking Professional Help:
Recognizing warning signs early on empowers individuals to take proactive steps toward a healthier lifestyle. It's important to approach weight management holistically, addressing both physical and psychological aspects. Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals, nutritionists, and mental health experts can provide personalized strategies for long-term success.
Conclusion:
Recognizing the warning signs of obesity is crucial for maintaining optimal health and preventing associated complications. If you or someone you know exhibits these signs, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide guidance on lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, and appropriate medical interventions. By being proactive in addressing obesity, individuals can significantly improve their overall well-being and reduce the risk of obesity-related health issues.

No comments:
Post a Comment